Disappointing, Some Value, October 22, 2008
Disappointing, Some Value, October 22, 2008
Gregory F. Treverton
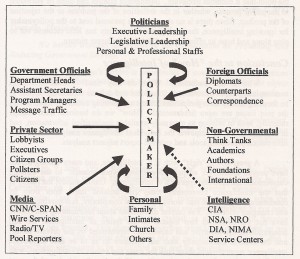
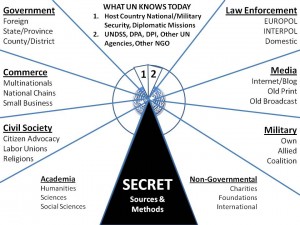
There are six (6) pages in this work that held my attention: pages 11-12 (Table 2.2 Analytic Concerns, by Frequency of Mention); page 14 (Figure 3.1, A Pyramid of Analytic Tasks); page 20 (Table 3.1, Wide Range of Analytical Tools and Skills Required); page 34 (Figure 5.1, Intelligence Analysis and Information Types), and page 35 (Table 5.1, Changing Tradecraft Characteristics). Print them off from the free PDF copy online (search for title).
My first review allotted two stars, on the second complete reading I decided that was a tad harsh because I *did* go through it twice, so I now raise it to three stars largely because pages 11-12 were interesting enough to warrant an hour of my time (see below). This work reinvents the wheel from 1986, 1988, 1992, etcetera, but the primary author is clearly ignorant of all that has happened before, and the senior author did not bother to bring him up to speed (I know Greg Treverton knows this stuff).
Among many other flaws, this light once over failed to do even the most cursory of either literature or unclassified agency publication (not even the party line rag, Studies in Intelligence). Any book on this topic that is clueless about Jack Davis and his collected memoranda on analytic tradecraft, or Diane Webb and her utterly brilliant definition of Computer Aided Tools for the Analysis of Science and Technology (CATALYST), is not worthy of being read by an all-source professional. I would also have expected Ruth Davis and Carol Dumaine to be mentioned here, but the lack of attribution is clearly a lack of awareness that I find very disturbing.
I looked over the bibliography carefully, and it confirmed my evaluation. This is another indication that RAND (a “think tank”) is getting very lazy and losing its analytic edge. In this day and age of online bibliography citation, the paucity of serious references in this work is troubling (I wax diplomatic).
Here are ten books–only one of mine (and all seven of mine are free online as well as at Amazon):
Informing Statecraft
Bombs, Bugs, Drugs, and Thugs: Intelligence and America's Quest for Security
Best Truth: Intelligence in the Information Age
Early Warning: Using Competitive Intelligence to Anticipate Market Shifts, Control Risk, and Create Powerful Strategies
The Art and Science of Business Intelligence Analysis (Advances in Applied Business Strategy,)
Analysis Without Paralysis: 10 Tools to Make Better Strategic Decisions
Strategic and Competitive Analysis: Methods and Techniques for Analyzing Business Competition
Lost Promise
Still Broken: A Recruit's Inside Account of Intelligence Failures, from Baghdad to the Pentagon
The New Craft of Intelligence: Personal, Public, & Political–Citizen's Action Handbook for Fighting Terrorism, Genocide, Disease, Toxic Bombs, & Corruption.
On the latter, look for “New Rules for the New Craft of Intelligence” that is free online as a separate document. Both Davis and Webb can be found online because I put them there in PDF form.
The one thing in this book that was useful, but badly presented, was the table of analyst concerns across nine issues that did not include tangible resources, multinational sense-making, or access to NSA OSINT.
Below is my “remix” of the table to put it into more useful form:
54% Quality of Intelligence
54% Tools of intelligence/analysis
43% Staffing
43% Intra-Community collaboration and data sharing
41% Collection Issues
38% Evaluation
32% Targeting Analysis
30% Value
Above are the categories with totals (first initial below connects to above). The top four validate the DNI's priorities and clearly need work.
32% T Targeting Analysis is important
30% V Redefine intelligence
30% Q Analysis too captive to current
30% To Directed R&D for analytic technology needed
27% T Targeting needs prioritization
27% S Analyst training important and insufficient
22% V Uniqueness
22% E PDB problematic as metric
22% To “Tools” of intelligence analysis are poor
22% To “Tools” limit analysis and limited by culture
The line items above are for me very significant. We still do priority based collection rather than gap-driven collection, something I raised on the FIRCAP and with Rick Shackleford in 1992. Our analysts (most of them less than 5 years in service) are clearly concerned about both a misdirection of collection and of analysis, and a lack of tools–this 22 years after Diane Webb identified the 18 needed functionalities and the Advanced Information Processing and Analysis Steering Group (AIPASG) found over 20 different *compartmented* projects, all with their own sweetheart vendor, trying to create “the” all-source fusion workstation.
19% C S&T underused, needs understanding
16% E Critical and needs improvement
14% E Assess performance qualitatively
14% Q Quality of analysis is a concern
14% Q Intelligence focus too narrow
14% S Language, culture, regional are big weaknesses
11% A Leadership
11% L Must be improved
11% Q Problem centric vice regional
11% Q Global coverage is important
11% C Open source critical, need new sources
11% I Lack of leadership and critical mass impair IC-wide
11% I IC information technology infrastructure needed
11% I Non-traditional source agencies need more input
8% V Unclear goals prevail
8% T Targetting analysis needs attn+
8% C Collection strategies/methods outdated
8% S Concern over lack of staff or surge capability
8% S Intelligence Community-wide curriculum desireable
8% I Should NOT pursue virtual wired network
8% I Security is a concern for virtual and sharing
5% E Evaluation not critical
5% Q Depth versus breadth an issue
5% Q Greater client context needed
5% C Law enforcement has high potential
5% S Analytic corps is highly trained better than ever
5% S Career track needs building
5% I Stovepiping is a problem, need more X-community
5% I Should pursue virtual organization and wired network
3% V Newsworthy not intelligence
3% L Radical transformation needed
3% E Metrics are not needed
3% E Evaluation is negative
3% E Audits are difficult
3% Q Long term shortfalls overstated
3% Q Global coverage too difficult
3% T Targeting can be left to collectors
3% C All source materially lacking
3% C Need to guard against evidence addiction
3% C Need to take into account “feedback”
3% S Should train stovepipe analysts not IC analysts
3% S Language and cultural a strength
For the rest, not now, but three at the bottom trouble me: the analysts do not have the appreciation for feedback; they do not understand how lacking they are in sources; and they don't know enough to realize that radical transformation is needed.
On balance, I found this book annoying, but two pages ultimately provocative.