Data Mining Wikipedia in Real Time for Disaster Response
My colleague Fernando Diaz has continued working on an interesting Wikipedia project since he first discussed the idea with me last year. Since Wikipedia is increasingly used to crowdsource live reports on breaking news such as sudden-onset humanitarian crisis and disasters, why not mine these pages for structured information relevant to humanitarian response professionals?
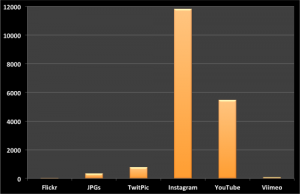
In computing-speak, Sequential Update Summarization is a task that generates useful, new and timely sentence-length updates about a developing event such as a disaster. In contrast, Value Tracking tracks the value of important event-related attributes such as fatalities and financial impact. Fernando and his colleagues will be using both approaches to mine and analyze Wikipedia pages in real time. Other attributes worth tracking include injuries, number of displaced individuals, infrastructure damage and perhaps disease outbreaks. Pictures of the disaster uploaded to a given Wikipedia page may also be of interest to humanitarians, along with meta-data such as the number of edits made to a page per minute or hour and the number of unique editors.
Fernando and his colleagues have recently launched this tech challenge to apply these two advanced computing techniques to disaster response based on crowdsourced Wikipedia articles. The challenge is part of the Text Retrieval Conference (TREC), which is being held in Maryland this November. As part of this applied research and prototyping challenge, Fernando et al. plan to use the resulting summarization and value tracking from Wikipedia to verify related crisis information shared on social media. Needless to say, I’m really excited about the potential. So Fernando and I are exploring ways to ensure that the results of this challenge are appropriately transferred to the humanitarian community. Stay tuned for updates.
See also: Web App Tracks Breaking News Using Wikipedia Edits [Link]